Tuesday, 31 January 2017
Pregnancy Care and Treatments
GOAL OF ANTENATAL CARE – HAPPY & HEALTHY MOTHER AND BABY
Pregnancy is divided into 3 trimesters for our convenience
1st trimester
|
2nd trimester
|
3rd trimester
|
Formation of Fetus
|
Growth of Fetus
|
Maturity around 37 weeks and preparatory stage for delivery
|
Fig 1.1 Pregnancy Care and Treatments
FIRST
TRIMESTER (Formation of Fetus) : - 1,2,3 months of pregnancy
History taking:
1)
Age
2)
Married life
3)
LMP : EDD
4)
CONSANGUINEOUS / NON-CONSANGUINEOUS
5)
History of previous pregnancies
6) Any medicines using for Diabetes, Hypertensions,
Hypothyroidism, Epilepsy,
Asthma or
Psychiatric problems.
7) Family History of Diabetes, Hypertension, Twins,
Anomaly babies.
8) Weight, BP, look for Anemia and swelling of feet.
Routine investigations:-
HB%, Blood group, Urine
Micro, RBS, T4, TSHScreening tests – HBsag, Tridot,HCV, VDRL
Scan:-
a) Dating Scan:- To the site of
pregnancy, Gestational age, Viability fetus.
b) NT Scan (11-13 weeks):- To rule out down’s Syndrome.
Double Marker Test:-
Done in patients aged > 35years
& in all precious pregnancies to
rule out down’s syndrome
AVOID:-
Sexual contact, Spicy food, Weight lifting, Journeys.
MEDICINES:-
Folic
Acid, B12 (B-complex)
Fig 1.2 First Trimester during pregnancy
Any other drugs
should be used only with Doctor’s Advice (Prescription).
SECOND
TRIMESTERS (GROWTH OF FETUS):- 4,5,6 Months of pregnancy
Routine Examination:- Weight, BP, Height of Uterus, Fetal heart rate
(Doppler)
Tests:-
- HB%, RBS/PPBS/GCT, Urine Micro
- Any infection in Urine à Advise to take more liquids and frequent voiding of Urine, keep nails cut.
- Repeated infection in urine à Urine culture/Sensitivity and add Antibiotics. White Discharge:- Anti Fungal, Anti Micro bials if warranted.
Fig 1.3 Second Trimisters during pregnancy
Scan:-
TIFFA SCAN(Targeted imaging for fetal anomalies) at 20 to 24
weeks
Most of the anomalies
can be identified during TIFFA Scan.
Limitation of Ultra Sono Graphy
1.
Some anomalies develop late in pregnancy
2. Some of the anomalies like Gastrointestinal tract
anomalies,Multiple Cardiac
anomalies are difficult to identify
3. Only structural anomalies can be identified,
functional anomalies like speech, hearing, vision can be identified only after
birth.
Fig 1.4 Scan At pregnancy
MEDICINES:
1.
Iron tablets from 4th month - To prevent Anemia
2.
Calcium tables from 5th month – To
strengthen bones and teeth of baby
3.
DHA (Omega-3 fatty acids) from 7th month –
To improve IQ of baby.
Fig 1.5 Medicine to be followed in pregnancy
ALL THREE
MEDICINES CAN BE CONTINUED AFTER DELIVERY.
EXERCISES:
1.
Walking.
2.
Breathing exercises.
3.
Household work.
THIRD
TRIMESTER (Maturity of fetus around 37 weeks preparatory stage for delivery):- 7,
8, 9 Months of pregnancy.
CHECK UP:
- Till 7th month à Monthly Checkup
- 8th month à Once in 2 weeks checkup
- 9th month à Weekly once checkup
v Normal
weight gain is 2kg/month
v If more
than 2kg weight gain à look for
fluid retention in body seen as swellingof feet, face, abdomen, hands etc.
Fig 1.6 Trimesters of pregnancy
i) Mainly
pregnancy induced hypertension, Anemia, Hypoprotenaemia
ii) Rarely
Cardiac, Renal causes.
INCASE OF PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION/PREECLAMPSIA
1.
Patient should come for frequent checkup and should be
under close monitoring to prevent ECLAMPSIA.
2. To report immediately if there are any
imminent symptoms of Eclampsia like headache, blurred vision, Epigastric
pain(vomiting), decreased urine output, increased pedal edema.
3.
Advise à Diet, Rest
and treatment.
SCANS:-
Growth Scan – 8th Month
9th Month Scan – 37 weeks.
Emergency visits to hospital in 9th Month
Leaking, Bleeding, Fever, Pain Abdomen, Decreased Fetal
Movements
TESTS:-
- HB%, RBS/PPBS/GCT, Urine Micro
- At 35 weeks à BT, CT, Platelet count, Serum Creatinine, Serum Bilirubin
DIET DURING
PREGNANCY
Diet during pregnancy should be adequate to provide
1.
Good Maternal Health
2.
Optimum Fetal growth
3.
Strength and vitality during labour
4.
Successful lactation
Fig 1.7 Diet and Healthy food During Pregnancy
IRON
(40mg/day):-
· Increases oxygen carrying capacity in blood, prevents
– weakness infections Increases pain bearing capacity, improves lactation in
mothers, Decreases premature labour and low birth weight of the
baby.
1.
Heme iron
à Animal
Sources
à Red meat, egg, fish
2.
Non Heme Iron
à Vegetable
source
à Green
Leafy vegetables, Spinach, beans, peas, carrot,beetroot, tomato, potato, broccoli,
lentils.
à FRUITS:
Straw berry, Apple, Pear, Peach, Plums.
à IRON
BOOSTING FRUITS: Citrus, Melons, Guava
à DRY FRUITS:
Dates, Figs, Raisins
à SEEDS:
Almond, Cashew, Sunflower seeds, Pumpkin seeds, Jaggery,
Using iron
utensils for cooking.
CALCIUM:
(1000mg/day):
- Helps in building bones and teeth of baby
Sources:
Milk 300mg, Yogurt – 370mg, Cheese, Sesame seeds –
200mg,Spinach
– 250mg, Cabbage, Cauliflower, Broccoli, Orange – 60mg, Date –
15mg, Almonds, Figs, Raisins.
Calcium Absorption:
- Increased by Vitamin D and Magnesium.
- Decreased by salt, Coffee, Alcohol,
- Phytates (nuts and grains) and oxalates in spinach
PROTEIN (60grams/day):
- Building block of tissues
Milk – 8gm, Curd – 10gm, Cheese – 14gm, Lentil 1 cup – 15gm,
Beans 1 cup – 18gm, Nuts and seeds, Egg – 6gm, Chicken – 27gm, Fish – 23gm.
Fig 1.8 Protein During Pregnancy
FOLIC
ACID(400 Micrograms/day):
Prevents:
1.
Neural tube defect
2.
Down’s Syndrome
3.
Recurrent abortions
4.
Preeclampsia
5.
Low birth weight
Sources:-
- Lentils, Spinach and Orange.
OMEGA – 3
Fatty acids (DHA 300mg)
Fetus:-
1.
Brain and Eye development
2.
Decrease low birth weight
3.
Decrease allergy and eczema
Mother:-
- Decrease pre-eclamptic toxemia, Depression
Sources:-
- Flax Seeds, Walnuts, Cold water fatty fish (Salmons, Sardine, Cod fish, HALIBUT)
Friday, 27 January 2017
STORIES ABOUT FOLLICULAR STUDY AND IRREGULAR PERIODS
This is
about lady with 28 years married for 5 years with irregular periods.
When we did follicular study follicles are not developing well. we increased
the dosage of cloniphene citrate from 50
to 200mg with added dosage of injection FSH. Still she had no proper growth of
follicles. I felt it was a very difficult case. She was also dejected and stopped
treatment.
Fig 1.1 Irregular periods Days
After one and half year she came again and I remembered her case; I
thought again the same problem might recur.
But she was happy and smiling. She said
her periods had become regular,
she wanted to go for follicular study that cycle .
Fig 1.2 Irregular Period Time and Worries
she also suggested that I
induce the cycle with 100mg clome tablets
as her periods have become regular. I was surprised but
obliged her, as there was some reasoning in it. To my astonishment the
follicles developed very nicely and ruptured at the optimum size of 20x23mm. Both
of us were happy about it and she conceived the same cycle. I asked how her periods became
regular and she had this story to tell.
Fig 1.3 Period Cycles and Treatments
She was a joint family .she was unemployed previously and her
husband had temporary job. To come to the clinic she had to ask her
mother-in-law for medical expenses; her co sisters would be grumbling to adjust
the household work whenever she came to the hospital. Coming to hospital was a
big ordeal for her. The follicle problem made her feel helpless and hopeless.
Fig 1.4 Normal Ovary and Polycystic ovaries comparison
Six months after stopping the treatment her husband got a permanent job and
they setup a separate family; she also started doing a job. There was a
financial freedom and no quarreling with co sisters. She was peaceful and
happy. She was busy doing household work and office work there was no time to
think and worry about pregnancy. She was surprised to find her periods becoming
regular for the past 6 months. After observing the regularity of the periods,
she felt that her periods improved and felt confident about herself and decided
to take treatment. This story made me understand that influence of emotions on
follicle growth.
Fig 1.5 Heavy Pain During Periods
Women was married for 10years with
history of irregular periods and pco. She had already undergone laparoscopy elsewhere for pco and
unfortunately her problem had recurred. She was not obese; I had given her
medicines and did follicular study there was no follicular growth. Women volunteered to undergo laparoscopy with me. She was very firm about the
decision. So I did repeat ovarian drilling ; after the surgery also ,though the
pco was cleared the periods was irregular and there was no improvement in
follicle growth.
Fig 1.6 Treatments for Ovaries
The surprising observation about her was that she never felt
dejected or cried. It seemed that she
has accepted the irregular periods. She was very cool and talked normally. She
never felt bad about the improper follicular growth, in
contrast to other prospective mothers with same problem, who used to feel
anxious and worried about follicular problem.
I asked about her (adamant
and persistent) irregular periods, when it started and other details and she
narrated her story. She used to have regular periods since menarche (the time
of attaining maturity). A few months before her marriage she developed heavy
bleeding and her mother took her to a doctor, who prescribed hormone pills ( 3
weeks pills).
Video 1.1 Andal Fertility Treatments for periods
She was advised to take the tablets for 3 months. She took the
pills for 1 month and the next month she went to her grandmothers place; there she went to the medical shop and ask
for the pill. The chemist who was their family friend told her, “ young girls like you should not use these tablets;
you have taken for 1 month! Don’t take it.”
so she felt guilty that she had
taken some dangerous pills that would have surely harmed her uterus. From then
on her periods became irregular. I could see
her firm belief that uterus and ovary were damaged was the reason for her irregular periods.
I told her that we use
such tablets some times for 6 months or more also depending on the necessity.
Unmarried girls also can safely use those pills , under supervision for right
indications. I convinced her if she believed my words backed with experienced
,she would surely get regular periods as her uterus and ovaries are as normal
as anybody else.
She appeared relieved;
and came after 3 weeks with periods without using any tablets. She was
surprised and happy. I advised her strongly to indulge in some hobby. She
started painting saries. her periods became consistently regular, with normal
follicular study and she conceived. Now she is having 2 children.
Tuesday, 24 January 2017
FAMILY PLANNING METHODS AND TREATMENT TO BE FOLLOWED
The term contraception includes
all temporary or permanent measures, to
prevent pregnancy .
Ideal contraceptive methods should fulfill the following criteria – widely acceptable, inexpensive, simple to use, safe, highly effective and requiring minimal motivation, maintenance and supervision.
TEMPORARY:
BARRIERMETHODS
IUCD(INTRAUTERINE contraceptive device)
OCP(oral contraceptive pill)
PERMANENT
MALE ---Vasectomy
FEMALE---Tubectomy
BARRIER
METHODS
·
Mechanical:
1. Male – Condom
2. Female – Condom, diaphragm, cervical cap
Chemical
(Vaginal contraceptives)
3. Creams – Delfen (nonoxynol-9, 12.5%)
4. Jelly – Koromex, Volpar paste
5. Foam tables – Aerosol foams, Chlorimin T or Contab, Sponge (Today)
Combination
Mechanical:
1. Male – Condom
2. Female – Condom, diaphragm, cervical cap
Chemical
(Vaginal contraceptives)
3. Creams – Delfen (nonoxynol-9, 12.5%)
4. Jelly – Koromex, Volpar paste
5. Foam tables – Aerosol foams, Chlorimin T or Contab, Sponge (Today)
Combination
Combined
use of mechanical and chemical
CONDOM
ADVANTAGES
|
DISADVANTAGES
|
May accidentally break or slip off
during coitus.
|
|
Inadequate sexual pleasure.
|
|
Easy to carry, simple to use and
disposable.
|
To discard after one coital act.
|
Useful where the coital act is
infrequent and irregular
Protection against sexually
transmitted diseases, e.g. gonarrhoea, Chlamydia, HPV and HIV
|
|
Protection against pelvic
inflammatory diseases
|
Failure rate – 14(HWY); 3(HWY) when
used correctly and consistently.
Precautions:
- To use a fresh condom for every act of coitus.
- To cover the penis with condom prior to genital contact
- Create a reservoir at the tip.
- To withdraw while the penis is still erect.
- To grasp the base of the condom during withdrawal.
Fig 1.4 Methods to stop Female Pregnancy
FEMALE CONDOM (FEMIDOM)
It gives protection against sexually
transmitted disease and pelvic inflammatory disease. It is expensive. Failure
rate is about 3-5/HWY.
VAGINAL
CONTRACEPTIVES:
The cream or jelly is introduced high
in the vagina . Foam tablets (1-2) are to be introduced high in the vagina at
least 5 minutes prior to intercourse.
VAGINAL
CONTRACEPTIVE SPONGE (Today)
It is made of polyurethane impregnated
with 1gm of nonoxynol-9 as a spermicide. Nonoxynol-9 acts as a surfactant which
either immobilizes or kills sperm. The sponge should not be removed for 6 hours
after intercourse. It’s failure rate is about 10/HWY.
RHYTHM
METHOD:
This method is based on identification
of the fertile period of a cycle and to abstain from sexual intercourse during
that period.
The first unsafe day is obtained by
subtracting 20 days from the length of the shortest cycle and last unsafe day
by deducting 10 days from the longest cycle.
Failure rate 20-30 (HWY)
Not applicable during lactational
amenorrhoea or when the periods are irregular
COITUS
INTERRUPTUS:
It necessitates withdrawal of penis
shortly before ejaculation. Accidental chance of sperm deposition
into the vagina. Failure rate – 20(HWY)
BREASTFEEDING,
LACTIONAL AMENORRHOEA (LAM)
Thus during breastfeeding, additional
contraceptive support should be given by condom, IUCD or injectable steroids
where available to provide complete contraception.
When the women is full breastfeeding, a
contraceptive method should be used in the 3rd postpartum month and with partial or no breastfeeding, she
should use it in the 3rd postpartum week.
full breastfeeding and amennorhoehic - risk of pregnancy <2% in first 6 months
general
--- risk of pregnancy 1- 10%
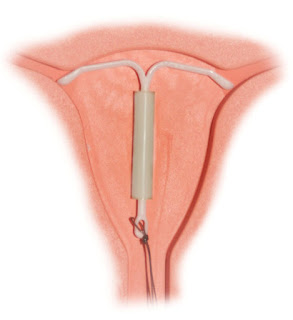
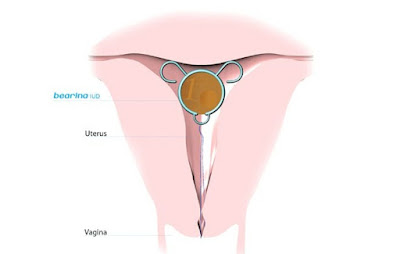
INTRAUTERINE
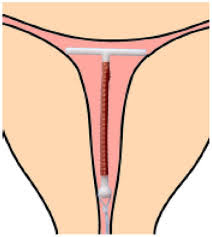
CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES(IUCD)
Cu T200B ------ replaced every 3 years
Cu T 380A:- ----Replacement every 10 years
Multiload Cu 250:- replacement every 3 years. Multiload Cu375 replaced every 5 years
Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS):-
n replaced every 5 years.
MODE
OF ACTION:
Video 1.1 Fertility and Treatments
- Biochemical and histological changes in the endometrium
- Copper devices – Preventing implantation through enzymatic interference.
- There may be increased tubal motility
- There may be impaired sperm ascent
- Levonorgestrel-IUS(Mirena) – It induces strong and uniform suppression of endometrium.
- Cervical mucous becomes very scantly.
- I is preferable to insert 2-3 days after the period is over.
CONTRA INDICATION FOR IUCD INSERTION
1)MENORRHAGEA
2)PELVIC INFECTION(PID)
3)DYSMENORRHOEA
factors related to its discontinuation
(10%-15%)
Pain, abnormal uterine bleeding and PID
SPONTANEOUS EXPULSION – The expulsion rate is about 5 percent.
FAILURE RATE–
The pregnancy rate with the device in situ is about 2 per 100 women years of use. Lowest
pregnancy rates are observed with Cu T 380A (0.8-HWY) and LNG-IUS (0.2 – HWY).
Fig 1.12 Contra indication for insertion
- 3rd generation IUCD(Cu T 380A, Multiload Cu375 and Levonorgestrel-IUS(Mirena)
- Higher efficacy with lowest pregnancy rate (less than one pre 100 women years).
- Longer duration of action (5-10 years)
- Low expulsion rate and fewer indications for medical removal.
- Risk of ectopic pregnancy is significantly reduced (Cu T-380A and LNG- IUS:0.02HWY)
- Non-contraceptive benefits specially with LNG-IUD
- Can be used as an alternative to hysterectomy for menorrhagia, DUB.
- Apart from the use of Cu T as a contraceptive, it is used following synaecolysis.
OCP(ORAL CONTRACEPTIVE PILLS) ----- NAMES
COMMERCIAL NAMES
|
COMPOSITION
|
No. of tablets
|
|
Progestin’s(mg)
|
Oestrogen (ug)
|
||
1.Mala N( Govt.of India)
|
Levonorgestreal 0.15
|
Ethinyl oestradiaol 30
|
21+7 Iron tablets
|
2.Mala- D
|
Levonorgestreal 0.15
|
Do
|
21+7 Iron tablets
|
3.Femilon (Infar)
|
Desogestreal 0.15
|
Ethinyl oestradiaol 20
|
21
|
4.Yasmin(Schering)
|
Drospirenone 3 mg (p.509)
|
Ethinyl oestradiaol 30
|
21
|
Depending on the amount of ethinyl
oestradiaol (E) and the types of progestin (p) used , pills are defines as: 1ST
GENERATION – With E 50 UG or more ; 2nd GENERATION -- with e 30- 35 ug and p as levonorgestrel or
norgestimate ; 3rd
GENERATION – WITH e 20- 30 ug and p as desogestrel or gestodene Low dose
pills have E less than 50 ug.
|
|||
HOW
TO PRESCRIBE A PILL:
New users should normally start their
pill packet on day one of their cycle.
FOLLOW
UP:
After 3months,6 months and yearly check up
necessary. The patient above the age 35 should be checked more frequently.
MISSED
PILLS:
When she misses two pills in the first
week (days 1-7), she should take 2 pills on each of the
next 2 days and then
continue the rest as schedule. Extra precaution has to be taken for next 7 days
either by using a condom or by avoiding sex.
If 2 pills are missed in the third week
(days 15-21) or if more than two active pills are missed at any time, another
form of contraception should be used as back up for nest 7 days as mentioned
above. She should start the next pack without a break.
If she misses any of the 7 inactive pills
(in a 28day pack only) she should throw away the missed pills. She should take
the remaining pills one a day and start the new pack as usual.
Indications for withdrawal : The
indication for withdrawal of the pill
are
2) Visual or Speech disturbance
3) Sudden chest pain
4) Unexplained fainting attack or acute vertigo
5) Serve
cramps and pain sin legs
6) Excessive weight gain
7) Severe depression
8) Prior
to surgery (it should be with held for at least 6 weeks to minimize
postoperative vascular complications).
9) Patient wanting pregnancy.
pill be continued :
A Woman who does not smoke and has no other risk factor for
cardiovascular disease , may continue the pill for 3 to 5 years is
considered enough and safe .
Failure rate:
1)Protection
against unwanted pregnancy (failure rate – 0.1 per 100 women year)
Non contraceptive benefits
: Improvement of menstrual
abnormalities – 1) Improvement of menstrual abnormalities
2) Reduction
of dysmenorrhea (40%)
3) Reduction of
menorrhagia (50%)
4) Reduction of
premenstrual tension syndrome (PMS)
5)
Reduction of Mittelschmerz’s syndrome.
6) Protein against iron deficiency anemia .
Video 1.2 Treatments in Andal Fertility clinic
12) Functional ovarian cysts
13) benign breast disease
14)
Osteopenia and postmenopausal osteoporotic fractures. Prevention of malignancies Endometrial cancer (50%)
18) Ovarian cancer
(40%)
19) Colorectal cancer (40%) This
protective effects persists for 10 -15 years even after stopping the methods
following a use of 6 months to 1 years .
SIIDE EFFECTS :
NAUSEA, VOMITING ,HEADACHE (OGN) AND LEG CRAMPS (PGN) : These are transient and often subside following continuous use for 2-3 cycles .
NAUSEA, VOMITING ,HEADACHE (OGN) AND LEG CRAMPS (PGN) : These are transient and often subside following continuous use for 2-3 cycles .
WEIGHT GAIN:
Though progestins have got an anabolic effects due to its chemical relation to testosterone, use of low dose COCs does not cause any increase in weight.
Though progestins have got an anabolic effects due to its chemical relation to testosterone, use of low dose COCs does not cause any increase in weight.
MENSTRUAL ABNORMALITIES -
·
Breakthrough
bleeding
is commonly due to sub threshold blood level of hormones
other causes
of break through bleeding in pill takers are
1) disturbance of drug absorption – diarrhea , Vomiting
2)use of enzyme inducing drugs (mentioned earlier) , missing pills, use of low does pills
3) pregnancy complications
4) Diseases -- cervical ectopy or carcinoma.
·
1) disturbance of drug absorption – diarrhea , Vomiting
2)use of enzyme inducing drugs (mentioned earlier) , missing pills, use of low does pills
3) pregnancy complications
4) Diseases -- cervical ectopy or carcinoma.
·
Amenorrhea:
Post pill amenorrhea of more than 6 months duration occurs in less than 1 percent cases. The association is casual not casual .it is usually more in women with per-existing functional menstrual disorders.
Post pill amenorrhea of more than 6 months duration occurs in less than 1 percent cases. The association is casual not casual .it is usually more in women with per-existing functional menstrual disorders.
Hypertension: Current low dose COC5
rarely cause significant hypertension. Pre-existing Hypertension is likely to
be aggravated.
VASCULAR COMPLICATIONS (OGN):
Venous thromboembolism (vtm) - the overall risk is to the extent of 4-6
times more than the non –users .pre-existing hypertension, diabetes , obesity
and elderly patient (over 35 specially with smoking habits ) are some of the
important risk factors ethinyl oestrodiol
in preference to menstranol and the reduction of the dose of the oestrogen
compound to 20 ug in the pill markedly reduce the incidence
Plasma lipids and lipoproteins are increased .total cholesterol and
triglycerides are increased .Preparation with more selective, lipid friendly
and third generation progestin’s namely desogestrel, gestodeone or norgestimate,
HDL Level is some what elevated .
VITAMINS AND MINERALS:
Vitamins b6,b12,
folic acid ,calcium , manganese, zinc and ascorbic acid levels are
decreased while vit a and vit k levels
are increased.
INJECTABLE PROGESTINS:
NET –EN IN A DOSE OF 200 MG GIVEN AT TWO – MONTHLY INTERVELS.DMPA 150 mg three monthly intervals.
NET –EN IN A DOSE OF 200 MG GIVEN AT TWO – MONTHLY INTERVELS.DMPA 150 mg three monthly intervals.
Mechanism of action :
1) Inhibition of ovulation by suppressing the mid cycle LH Peak
2) cervical mucous becomes thick and viscid therapy prevents sperm penetration
3) Endometrium is atrophic preventing blastocyst implantation
1) Inhibition of ovulation by suppressing the mid cycle LH Peak
2) cervical mucous becomes thick and viscid therapy prevents sperm penetration
3) Endometrium is atrophic preventing blastocyst implantation
Fig 1.14.a. Ingectible Progestins
Advantages :
1)it eliminates regular medication as imposed by oral pill
2) it can be used safely during lactation.
Disadvantages :
There is chance of
irregular bleeding and occasional phase of amenorrhea. Loss of bone
mineral
density has been observed with along term use of depot provera.
OTHER EFFECTS :
Weight gain and Headache
Weight gain and Headache
EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION
·
Hormones
·
IUD
·
ANTIPROGESTRONE
·
OTHERS
POST COITAL CONTRACEPTIVE
DRUGS
|
Dose
|
Pregnancy rate (%)
|
Levonorgestrel
|
O.75 MG STAT AND AFTER 12 HOURS
|
0-1
|
Ethinyl oestrodiol 30ug + Norgestrel 0.25 mg
|
2 TAB STAT AND 2
AFTER 12 HOURS
|
0-2
|
Mifepristone
|
100 MG SINGLE DOSE
|
0-0.6
|
Copper IUDs
|
Insertion within 5 days
|
0-0.1
|
Levonorgestrel 0.75 MG ,two doses given
at 12 hours intervals , is very successful and without any side effects .
No fetal adverse effects has been
observed when there is failure of emergency contraception
Mode of action
·
Ovulation is either prevented or
delayed when the drug is taken in the beginning of the cycle
·
Fertilization is interfered
·
Implantation is prevented as the
endometrium is rendered unfavorable.
·
Interferes with the function of corpus luteum or may
causes luteolysis.
Draw backs:
Nausea and vomiting are much more intense with
oestrogen use
Copper IUD:
Introduction of copper IUD within a maximum
period of 5 days can prevent conception following accidental unprotected
exposure .this prevent implantation.
Anti progesterone:
Anti progesterone binds competitively to
progesterone receptors and nullifies the effects of endogenous progesterones.
PERMANENT METHODS
The operation done on
male is vasectomy and that on the female is tubal
occlusion, or tubectomy
occlusion, or tubectomy
VASECTOMY
Advantages:
1) The operation can be done as an outdoor procedure
2) Failure rate is minimal – 0.15
percent and there is a fair chance of success of reversal anastomosis operation
(50%)
Female : TUBECTOMY
Puerperal:- 24-48 hours after delivery
Interval: 3 months after delivery. It is done after periods
Concurrent:
done along with termination of pregnancy
done along with termination of pregnancy
Open—pomeroy’s method failure rate .1-.3%
Lap—rings failure
rate-.2--.6%
Contraceptive prescription
should be on individual basis. In an individual , Method may vary according to
her phase of reproductive life .Teenage girls, Older women should also be
protected.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)